In 2018, enterprises will spend $178 billion on public cloud services, an increase of 22% over 2017. Once enterprises move to the cloud, the real work of cloud management begins. Here are four challenges that confront IT teams when working with cloud infrastructure services:
- Cloud Operations. How do you monitor, configure, and secure cloud workloads? How do you handle availability for enterprise applications built on different cloud services?
- Cloud Budgeting. How do you not overspend on cloud services? How do you select the right cloud workload at the right price at the right time?
- Cloud Talent. Where do you find the right people to build, operate, and maintain cloud workloads? How does your team keep up with the rapid pace of cloud innovation?
- Multi-Cloud Management. How do you avoid relying on a single cloud platform vendor? How do you manage multi-cloud environments at scale?
 Figure 1 - How Operations, Cost, and Skill Deficits Are Holding Back Cloud Adoption.
Figure 1 - How Operations, Cost, and Skill Deficits Are Holding Back Cloud Adoption.
In our recent webinar, 451 Research’s Owen Rogers and OpsRamp’s Mahesh Ramachandran, highlighted key trends on the state of enterprise cloud adoption. The two thought leaders discussed common roadblocks for cloud adoption and offered strategies to overcome them. We recommend you watch the entire presentation - which includes Owen’s insights on cloud challenges and Mahesh’s principles for cloud management - in the video below.
What’s Holding Back Cloud Adoption?
The cloud has brought a new set of challenges for IT teams. While enterprises expected to achieve cost savings, agility, scalability, and availability with cloud adoption, the reality has been a bit different.
The big pain points for enterprise cloud adoption are budgeting (60%), meeting business demands (48%), security (46%), and skill shortages (43%). When it comes to cloud expertise, IT decision makers rate cloud security (60%), platform expertise (50%), cloud administration (45%), and cloud architecture (39%) as the must-have skills. Finally, 80% of enterprises are finding it either very difficult or moderately difficult to hire experienced cloud professionals.
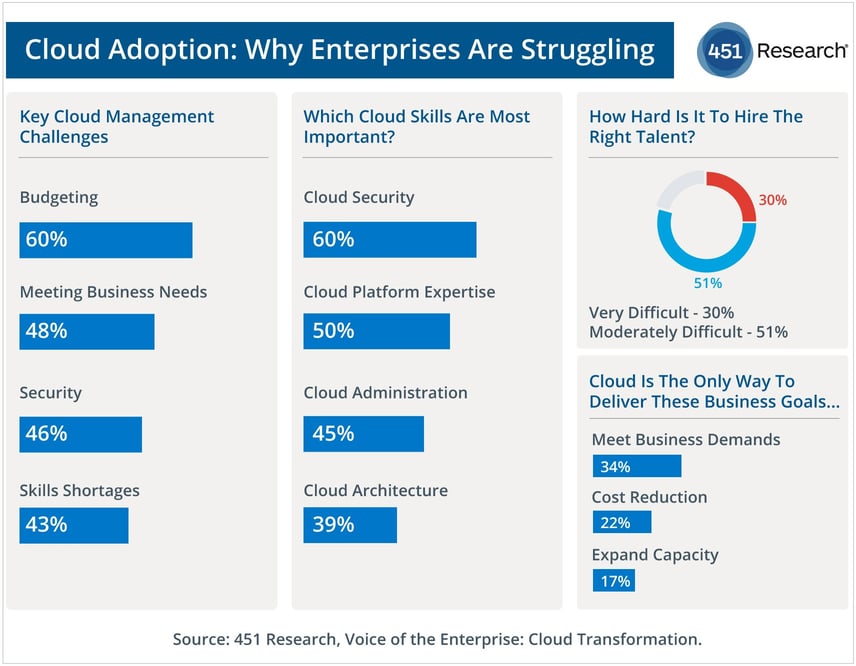
Figure 2 - Enterprises Are Yet To Come To Terms With Cloud Management.
What’s Different About Cloud Management?
When it comes to cloud management, enterprises are still applying old ways of thinking to a new problem. Cloud management is all about handling cloud operations and cloud spending at scale.
IT teams need to understand the complexity of modern cloud environments. The interplay between different cloud constructs and the moving parts behind each cloud service makes cloud operations doubly challenging:
- Cloud Services Are Architected Differently. The cloud brings in a new set of constructs in the form of S3 bucket stores, Lambda functions, and different platform services. In the cloud, there are many more constructs that IT teams need to manage. You need to correctly configure and monitor each cloud construct, which involves a discrete set of tasks that’s quite different from on-premises management.
- Cloud Services Are Updated Frequently. AWS delivered 1,300 new services and features in 2017 alone, 30% more than in 2016. Cloud services have many different moving parts, which are always changing. Apps built on cloud native services have 10x more moving parts as compared to a legacy application.
RightScale estimates that companies are wasting $10 billion annually on cloud spending. Budget overruns are the norm when procuring cloud assets is frictionless. Here's why it's hard to keep track of cloud spending:
- Instant Gratification. It’s easy to provision a cloud resource as it is a simple command line away. Business units can instantly spin up cloud services as long as they have access to a credit card.
- Procurement Process. Lengthy approval cycles were common for datacenter purchases. You would prepare a business case, issue a request for proposal, and shortlist vendors before you had access to computing power. You can buy cloud services today without a business case, IT oversight, or spending justifications.
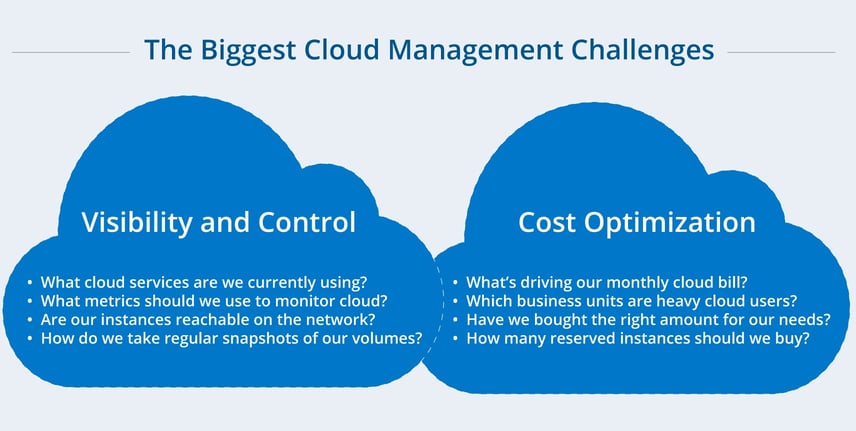
Figure 3 - Cloud Operations and Cost Optimization: Twin Challenges For Cloud Management.
Cloud Management: Two Principles For Success.
Enterprises need a new framework to overcome their cloud management challenges. Here are two principles that IT teams will need to master to manage cloud environments:
- Manage Only By Exception. The goal of managing cloud environments should be not to manage them at all. The only time humans should work on cloud operations is to handle exceptions. If you have thousands of cloud resources, admins should handle only a tiny fraction (< 1%) of cloud assets.
- Adjust Resources To Demand, Continuously. You’ll need the ability to dynamically adjust cloud supply to the demands of your applications. Understand the different sources of application demand and match it to your cloud supply chain for agile capacity management.

Figure 4 - Get A Handle On Hyperscale Cloud Management With These Two Principles.
How do you apply these two principles to cloud operations and cloud spending?
- Cloud Operations. Monitoring and configuration management are two primary tasks performed every day by cloud teams.
- Monitoring. While there’s plenty of instrumentation (metrics, logs, or data) on the cloud, the trick is to select the right points of observation. Once you’ve selected the right observation points, identify the correct exception conditions. You’ll need deep knowledge of your applications and the ability to recognize when things go wrong to map your exception conditions. Once you select the exception conditions, leverage smart tooling to flag exceptions. The right management tools help you scale cloud operations by reducing the number of cloud assets a human operator needs to oversee.
- Configuration Management. Configurations refer to settings on your cloud assets. Configuration complexity increases with variations across configuration settings. Automate configuration generation for your cloud resources using policies. Once you automatically generate configurations, check, enforce, and drive the desired configuration state using an enforcement mechanism. Enforcement prevents unnecessary exception errors and reduces manual operations for cloud management.
- Cloud Cost Optimization. Enterprises will need to study demand patterns for individual applications and understand aggregate demand across enterprise workloads. You can make realistic cloud procurement decisions only when you can predict individual and aggregate demand. Study application specific demand patterns (cyclical, steady, or waning) to buy the right type of cloud resources. Become a smart shopper by right sizing, decommissioning, or using different instance types to optimize cloud spending.
Our blog post addresses only a few cloud management topics discussed in the webinar. To get the whole picture, check out the video above or browse through the slide deck below:
Next Steps:
- Read the Blog : Discover, Scale, And Optimize Your Multi-Cloud Infrastructure With OpsRamp
- Learn about OpsRamp's Hybrid Infrastructure Monitoring solution
- Schedule a custom demonstration with a solution consultant today.