Just like public clouds, private clouds deliver on-demand, self-service, and elastic infrastructure. You gain higher levels of security, privacy, and compliance as compared to public clouds.
Private cloud adoption has been a controversial topic in the tech industry. Over the years, private cloud has had its advocates and critics. Here are five facts that set the record straight on private cloud:
Myth #1. Private Cloud Growth Is Keeping Pace With Public Cloud Adoption.
Fact. Wikibon estimates that the market for public cloud is 3.5 times bigger than private cloud. In 2015, the private cloud market hit $7 billion while public cloud touched $25 billion. In fact, AWS, the leading IaaS vendor, alone clocked $7.88 billion in revenues last year.
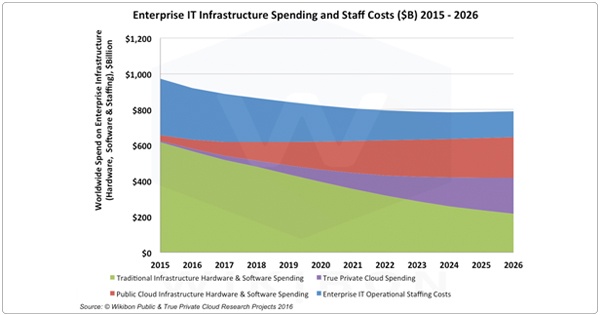
Source: Wikibon
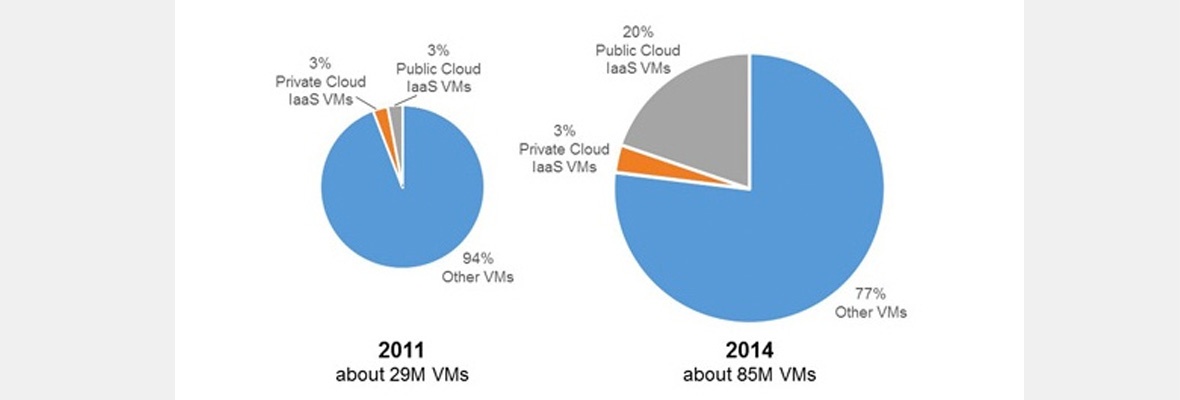
In 2011, Gartner found the number of virtual machines (VMs) in public cloud IaaS and private cloud IaaS were equal at 3%. By 2014, public cloud IaaS VMs had grown to 20% (over a larger base) while private cloud IaaS VMs were still at 3%.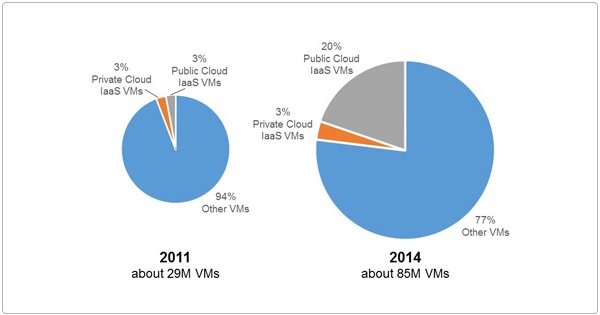
Source: Gartner
Myth #2. Private Cloud Is Dead.
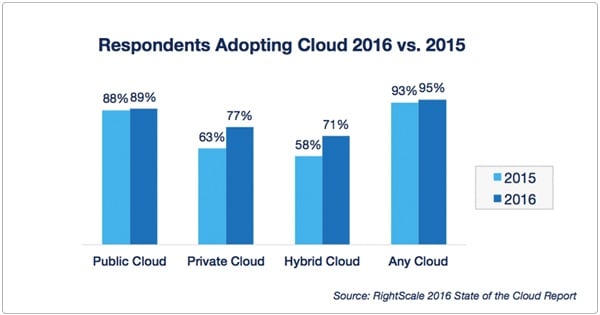
Fact. While private cloud isn't growing as fast as expected, the reports of its death have been highly exaggerated. IT teams are using private clouds for both Mode 1 and Mode 2 applications. Rightscale's 2016 State of the Cloud Survey found that private cloud adoption increased from 63 percent to 77 percent. On an average, enterprises today use three public and three private clouds.
Source: RightScale
Myth #3. Private Clouds Are Easy To Implement.
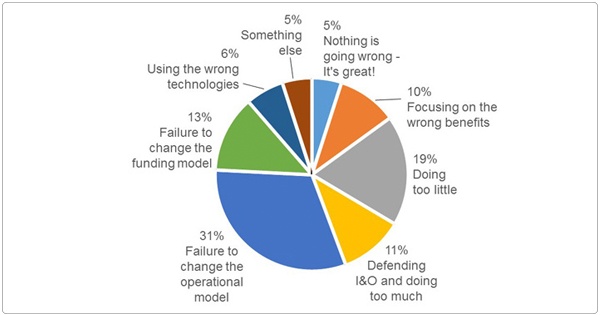
Fact. Your private cloud initiative will fail if you don't change your operating model. Thomas Bittman surveyed Gartner’s Datacenter conference attendees to understand why private clouds were not yielding the desired results. Private cloud failures have more to do with organizational and cultural issues than with technology. Bittman’s take: “Jamming cloud into your existing process model and org structure ain’t gonna work.”
Source: Gartner
Myth #4. There Are No Successful Private Clouds.
Fact. There's a temptation to completely write off private clouds. Enterprises have increased agility and innovation and aligned with business goals using private clouds. FedEx, Revlon, Disney, PayPal, and GoDaddy are examples of successful private cloud deployments.
.@PayPal deploys ~1,000 times a day. 10k+ physical servers running Openstack #GartnerDC pic.twitter.com/9crVp4NgIl
— Abner Germanow (@abnerg) December 9, 2015
Myth #5. OpenStack Is The Only Sheriff In Town.
Fact. OpenStack has emerged as the most prominent open source private cloud architecture. Walmart, American Express, Bloomberg, Best Buy, and The Gap are OpenStack customers. 451 Research has predicted that global OpenStack revenues will hit $3.3 billion by 2018.
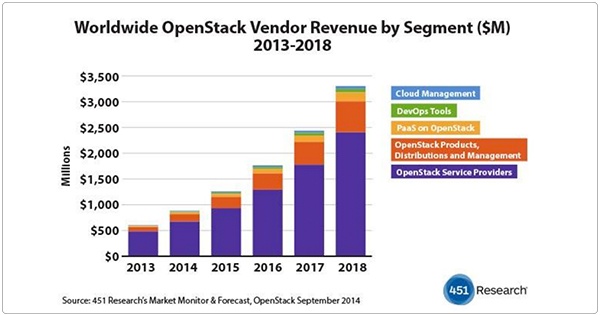
Source: 451 Research
This doesn't mean that there are no viable competitors for OpenStack. IT vendors like VMware, HP, EMC, and Cisco, and open source initiatives like CloudStack and OpenNebula offer compelling private cloud alternatives.